Introduction
Patients with relapsed or refractory (r/r) DLBCL had poor prognosis when ineligible to autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HSCT). Polatuzumab vedotin (Pola) has demonstrated significant efficacy and acceptable safety in such patients in Clinical trials and real-world data. Here we reported long-term follow-up result of Pola-based regimen in real-world Chinese cohort.
Aims
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Pola-based regimens for the treatment of r/r DLBCL using real-world data.
Methods
This retrospective study analyzed data from the Chinese Pola compassionate use program, conducted at four tertiary hospitals from December 2019 to June 2021. Patients with r/r DLBCL were enrolled. The treatment regimens included Pola in combination with rituximab (Pola+R) or with additional bendamustine (Pola+BR) administered for six cycles, with each cycle lasting 21 days. The objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and adverse events (AEs) were analyzed.
Results
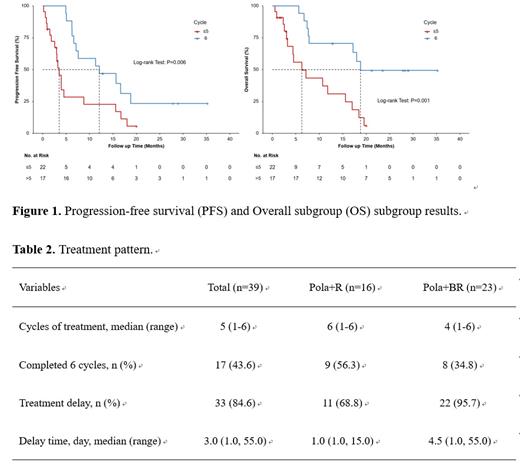
Thirty-nine patients were included in the analysis, with a median follow-up of 23.5 months (range: 0.6-35.2). The ORR at the end of treatment was 38.5% (15/39), while the best ORR achieved was 69.2% (27/39). The median PFS and OS were 6.6 months (95%CI: 3.7-9.6) and 15.6 months (95%CI: 3.4-27.9), respectively. Compared to those who did not complete six cycles of treatment, a significantly longer PFS (12.1 vs. 3.5 months, P=0.006) and OS (18.8 vs. 6.3 months, P=0.001) was observed in patients who completed all six cycles of treatment. Among 16 patients receiving Pola+R and 23 receiving Pola+BR, the proportion of patients who completed all six-treatment cycles was 56.3% and 34.8%, respectively. Grade 3-4 AEs were reported in 48.7% of patients with most commonly occurred being neutropenia (28.2%), leucopenia (17.9%) and thrombocytopenia (15.4%).
Conclusions
The 2-year follow-up analysis demonstrated sustained progression-free and overall survival, with no new safety signals. The full cycles of Pola-based regimen may contribute to better efficacy for real-world populations. These findings supported Pola-based regimens as an effective real-world treatment option for Chinese patients with r/r DLBCL.
Key words
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; refractory/relapsing; polatuzumab vedotin; real-world study; China.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.